Insurance subrogation guide is one of the most important processes in the insurance world, yet many policyholders don’t fully understand how it works. When your insurance company pays a claim for damages caused by someone else, it can legally pursue the at-fault party to recover the money. This process is known as subrogation.
Subrogation protects insurance companies from unnecessary loss and helps keep insurance premiums lower for everyone. This guide explains insurance subrogation in simple terms, including advantages, disadvantages, real-world examples, FAQs, and SEO-friendly elements.
The right of an insurance company in the United States to lawfully step into the shoes of their insured to seek reimbursement from a negligent third party following payment of a claim is called insurance subrogation. The insurance company can recover its expenses from the at-fault party’s insurance company using this procedure, which could result in a deductible refund for the insured. Subrogation rests on the idea of assigning the financial responsibility to the party responsible for the loss, and so stopping the insured from double recovery.
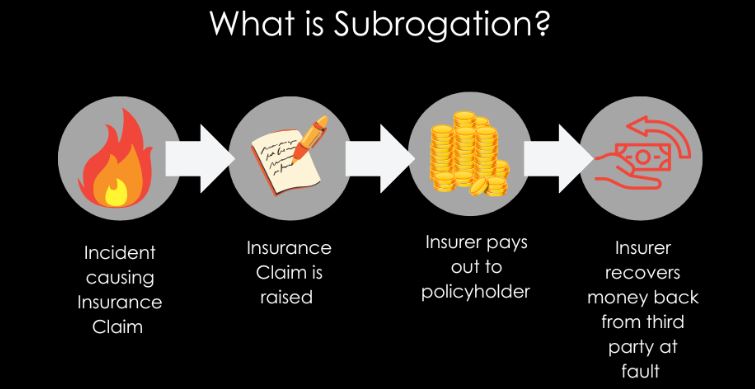
What Is Insurance Subrogation?
Insurance subrogation is the legal right that allows an insurance company to seek reimbursement from the responsible party after paying a claim to the insured.
Example: If another driver hits your car and your insurer pays for repairs, your insurer can pursue the at-fault driver’s insurance company to recover the payment. In other words, insurance firms can sue third parties liable for losses to recoup their costs via subrogation. This helps the insurer pay claims files from its insurers faster, then pursue the total claim from the party at fault for the loss. Subrogation allows policyholders to receive benefits more quickly and helps maintain low rates.
Common in auto, property, casualty, and healthcare insurance, subrogation simplifies settlements by helping to expedite them.

Pros & Cons of Insurance Subrogation
Pros
- Helps lower insurance premiums by recovering costs from at-fault parties.
- Protects policyholders from paying out-of-pocket upfront.
- Makes claims quicker since insurers can pay you first and recover later.
- Encourages accountability by holding the responsible party financially liable.
- Often leads to deductible reimbursement for the insured.
Cons
- Delays in deductible refunds until subrogation is completed.
- Legal disputes may slow down the recovery process.
- Not all claims qualify, especially if fault cannot be proven.
- Policyholders may be required to assist, such as providing statements or documentation.
Possible complications if both parties share fault (comparative negligence).

Why Insurance Subrogation Matters
Subrogation plays a major role in:
- Auto insurance
- Homeowners and renters insurance
- Health insurance
- Property and casualty insurance
It ensures fairness and financial balance across the insurance industry.

Conclusion
Insurance subrogation guide is a behind-the-scenes process that benefits both insurers and policyholders. By allowing insurance companies to recover payments from the responsible parties, subrogation helps maintain affordable premiums and speeds up claim payouts. Understanding how it works can help you know what to expect—especially regarding deductible refunds and claims handling. Overall, subrogation is a vital mechanism that promotes fairness and accountability in insurance.
FAQs
1. Do I get my deductible back through subrogation?
Yes. If your insurance company successfully recovers money from the at-fault party, you usually receive your deductible back.
2. How long does subrogation take?
It can take anywhere from a few weeks to several months, depending on fault disputes, documentation, and insurer cooperation.
3. Can I refuse subrogation?
Most insurance policies include a “subrogation clause,” meaning you legally cannot prevent your insurer from pursuing reimbursement.
4. Does subrogation affect my premium?
Successful subrogation may help prevent premium increases because your insurer recovers the payout.
5. What happens if the at-fault party has no insurance?
Your insurer may still pursue them directly, but recovery may be difficult. Uninsured motorist coverage can help in these situations.



